揭秘高血压
Hypertension has become an important public health issue globally, with its high morbidity and wide range of complications, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease, making it a major concern. With changes in lifestyle, an aging population, and environmental factors, the prevention and control of hypertension is becoming increasingly challenging.
Current Status of Hypertension Drug Therapy
Hypertension is a common chronic disease, and long-term hypertension increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Currently, the main antihypertensive drugs used clinically include diuretics, vasodilators, and central inhibitors.
Diuretics
Diuretics promote the kidneys to excrete more urine, reduce the water content in the blood, thereby lowering the total blood volume, and achieve the purpose of lowering blood pressure. Common diuretics include thiazide and cycloalkane types.
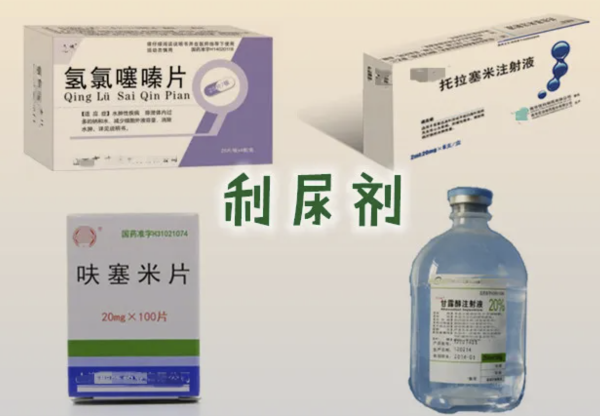
Side effects: mainly include electrolyte imbalance, hypokalemia, hyperuricemia, and impaired glucose tolerance. Long-term use may cause kidney damage.
Vasodilators
Vasodilators interfere with the signal transmission of vasoconstriction, block receptors, thereby dilating blood vessels, reducing peripheral vascular resistance, and achieving the effect of lowering blood pressure. It mainly includes the following categories:
- α-receptor blockers (sympathetic nerve inhibitors): such as terazosin and prazosin.

Side effects: include postural hypotension, dizziness, and fatigue.
- β-receptor blockers: such as the labetalol series.
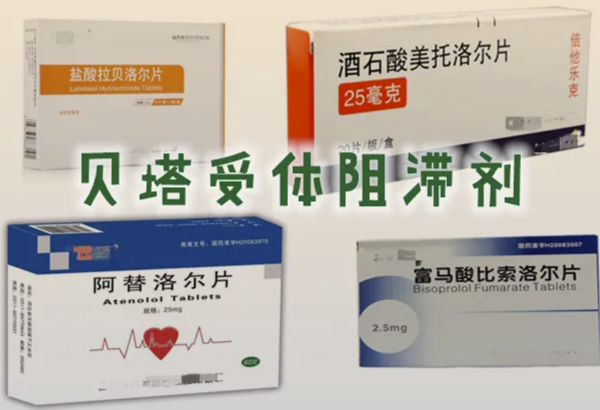
Side effects: may affect insulin secretion, and long-term use may increase the risk of diabetes.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI): such as lisinopril and enalapril.
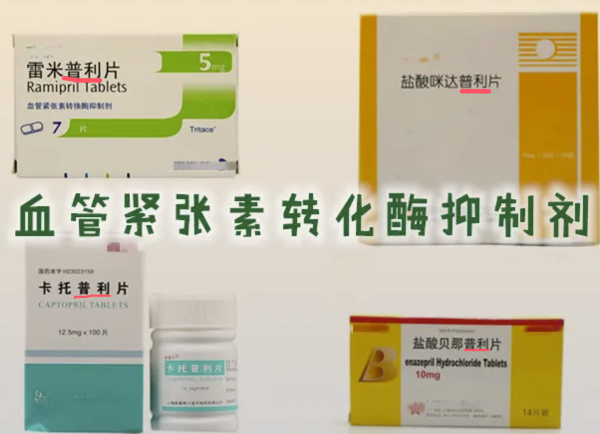
Side effects: cause cough, angioedema, and in severe cases, can lead to myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, and stroke.
- Calcium channel blockers: such as the dihydropyridine series, mainly inhibit the entry of calcium ions into cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cells to lower blood pressure.
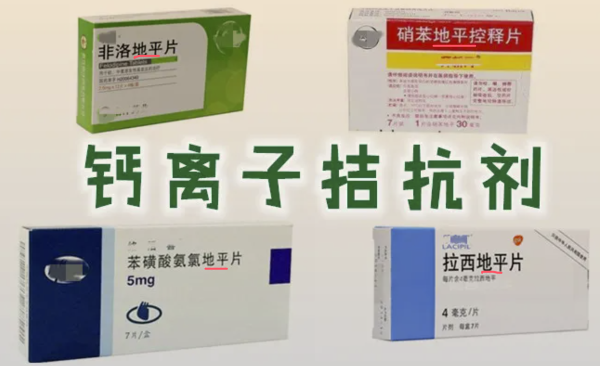
Side effects: include hemorrhoids, constipation, and heart disease.
Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment
Traditional Chinese medicine has a different understanding and treatment approach for hypertension, believing that its main causes include hyperactivity of liver yang, yin deficiency with yang hyperactivity, and phlegm-dampness obstruction. Traditional Chinese medicine usually classifies hypertension into several syndromes, such as liver yang hyperactivity, liver and kidney yin deficiency, and yin deficiency with yang hyperactivity.
Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment Methods
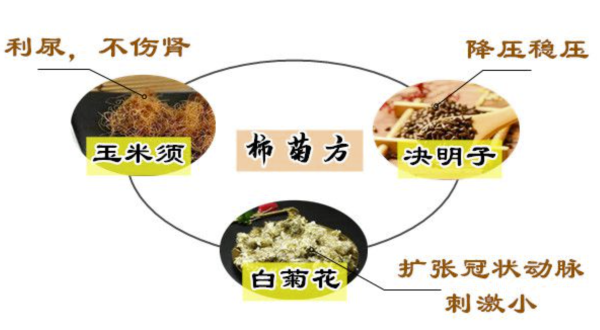
- Chinese herbal medicine regulation: For example, the Shizhu decoction, derived from the “Wanbing Huichun” by the great medical scientist Gong Tingxian in the Ming Dynasty, contains 10 grams of white chrysanthemum, 6 grams of Semen Cassiae, and 6 grams of corn silk, which has a clearing heat and diuretic effect.
- Acupuncture: By stimulating specific acupoints, such as Baihui and Zusanli, it regulates qi and blood, achieving a hypotensive effect. Acupuncture has shown good hypotensive effects in clinical practice.
Hypertension is a chronic disease that requires long-term regular medication. When choosing antihypertensive drugs, the patient’s age, comorbidities, and economic status should be fully considered to develop an individualized medication plan. At the same time, patients need to pay attention to medication compliance and regularly monitor blood pressure and adverse reactions. By combining traditional Chinese and Western medicine, blood pressure can be more effectively controlled and the patient’s quality of life improved.
高血压已成为全球公共卫生的重要问题,其高发病率和广泛的并发症,如心脏病、中风和肾脏疾病,令其备受关注。随着生活方式的改变、人口老龄化加剧及环境因素的影响,高血压的防控形势愈发严峻。
高血压药物治疗现状
高血压是一种常见的慢性疾病,长期高血压会增加心脑血管疾病的发病风险。目前,临床上常用的降压药物主要包括利尿剂、扩张剂和中枢抑制剂等。
利尿剂
利尿剂通过促进肾脏排出更多尿液,减少血液中的水分,从而降低血液总量,达到降压的目的。常见的利尿剂有噻嗪类和环烷酮类。

副作用:主要包括电解质紊乱、低钾血症、高尿酸血症及糖耐量受损等,长期使用可能对肾脏造成损害。
扩张剂
扩张剂通过干扰血管收缩的信号传导,阻滞受体,从而使血管扩张,降低外周血管阻力,达到降压效果。主要包括以下几类:
- α受体阻滞剂(交感神经抑制剂):如特拉唑嗪、哌唑嗪等。

副作用:包括体位性低血压、头晕和乏力等。
- β受体阻滞剂:如洛尔系列等。

副作用:可能影响胰岛素分泌,长期使用可能增加糖尿病风险。
- 血管紧张素转化酶抑制剂(ACEI):如赖诺普利、依那普利等。

副作用:引起咳嗽、血管性水肿,严重时可导致心梗、脑梗和中风等。
- 钙离子拮抗剂:如地平系列,主要通过抑制钙离子进入心脏和血管平滑肌细胞来降低血压。

副作用:痔疮、便秘和心脏病等。
中医药治疗
中医对高血压的理解与治疗方法有所不同,认为其主要病因包括肝阳亢盛、阴虚阳亢、痰湿阻逆等。中医通常将高血压分为多种证型,如肝阳亢盛型、肝肾阴虚型、阴虚阳亢型等。
中医治疗方法
中药调理:例如柿菊方,源于明代大医学家龚廷贤的《万病回春》,其成分包括白菊花10克、决明子6克、玉米须6克,具有清热利尿的作用。

针灸:通过刺激特定的穴位,如百会、足三里等,调节气血,达到降压效果。针灸在临床实践中显示出良好的降压效果。
高血压是一种需要长期规律用药的慢性病。在选择降压药物时,应充分考虑患者的年龄、合并症及经济状况,制定个体化的用药方案。同时,患者需注意用药的依从性,定期监测血压和不良反应。结合中西医治疗,能够更有效地控制血压,改善患者的生活质量。
